
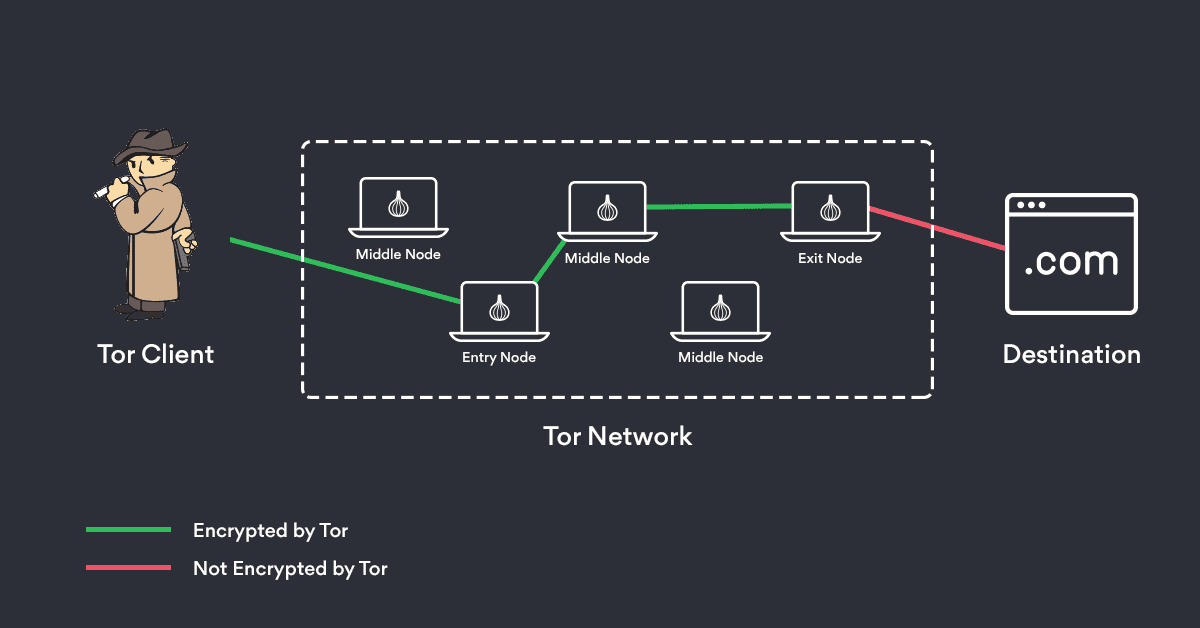
Using onion routing to protect critical assets Apple’s Private Relay feature embodies the same purpose as onion routing’s – protect the identity and online activities of the user. Traffic is sent through two separate, secure internet relays. Global companies like Apple have implemented features like Private Relay to protect your identity and online activities when using Apple’s Safari browser. Since its introduction 25 years ago, onion routing has been implemented in a number of services including virtual private networks, browser/web isolation, email, remote login, etc. The inherent characteristic of Tor enables threat actors to remain anonymous, making it difficult for organizations to effectively respond to cyberattacks. While Tor can provide privacy protection for individuals or groups seeking anonymity, it has also been used by criminal groups for illicit purposes such as malware distribution. It is an open-source, decentralized privacy network that is comprised of thousands of volunteer-run servers and enables users to browse the internet anonymously. Tor, short for “The Onion Router” is the largest and most well-known implementation of the onion network. Due to this design, the nodes cannot see other nodes in the network and only the final node (“exit node”) is able to determine its own location in the traffic chain. The process continues to the last node, where the final layer of encryption is removed and the original message is transmitted to its final destination. The current node does not know if the previous node is the originator or just another node, ensuring that the sender’s identity is kept anonymous. Each node only knows the location of the previous node along with the location of the next node. The technology gets its “onion” name from wrapping each message with layers of encryption which have to be “peeled off” or “unwrapped” at each node just like an onion.
Unlike VPNs, which typically use a single server to route your traffic, onion routing uses multiple routers or nodes, making it difficult for bad actors to trace the origin of the sender.

The encrypted data is transmitted through a series of nodes or routers to relay messages. In an onion network, the messages are encapsulated in multiple layers of encryption at the original entry node.

intelligence communication online, onion routing is a technique for anonymous communication over a computer network. What is onion routing?ĭeveloped in 1996 to protect U.S. In a recent webinar hosted by Security Week, “Internet Icons – The Inventors of Onion Routing,” the three founders of onion routing - David Goldschlag, Paul Syverson, and Michael Reed - discussed the motivations behind the development of the groundbreaking technology that has transformed how we secure online communications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
